This area provides general information on state debt and borrowing programs and details OBM’s roles regarding the issuance and management of state debt. The information is provided for reference only and is not a summary or compilation of information for any particular bond issue.
Types of State Debt
With limited exceptions, the Ohio Constitution prohibits the incurrence or assumption of debt by the state without a popular vote. The state may incur debt to cover casual deficits or failures in revenues, or to meet expenses not otherwise provided for, but this power is limited in amount to $750,000. The Constitution expressly precludes the state from assuming the debts of any county, city, town or township, or of any corporation (though an exception in both cases is for debts incurred to repel invasion, suppress insurrection, or defend the state in war). Issuance of state debt paid from the state’s general fund is subject to the Constitutional 5% debt service limitation.
By 20 constitutional amendments approved from 1921 to present, Ohio voters have authorized the incurrence of state general obligation (GO) debt and the pledge of taxes and excises to its payment. Exceptions or limitations are for highway user receipts which may only be used to pay debt service on bonds issued for highway projects and net state lottery proceeds which may only be used for debt service for public primary and secondary education facilities.
General Obligation Debt
Ohio Public Facilities Commission
The Ohio Public Facilities Commission issues general obligation bonds for common schools, higher education, natural resources, coal research and development, conservation projects, local infrastructure improvements, Third Frontier research and development, job-ready site development, and veterans’ compensation. Each of these currently authorized programs is described below.
Coal Research and Development - A 1985 constitutional amendment authorizes $100 million of general obligation debt to be issued to finance grants, loans, or loan guarantees for research, development, and implementation of coal technology that will encourage the use of Ohio coal. Funding is available to any individual, association, or corporation doing business, or to any educational or scientific institution located in the state. Additional debt may be issued as outstanding debt is retired, provided that not more than $100 million is outstanding at any time.
Common Schools - A 1999 constitutional amendment authorizes general obligation debt to be issued to pay the costs of school buildings and related capital facilities for a system of common schools throughout the state. There is no constitutional limit on the amount of debt that can be outstanding at any time. The full faith and credit, revenue (including net state lottery proceeds, if pledged) and taxing power (excluding highway user receipts) of the state are pledged to retire this debt.
Conservation - Constitutional amendments in 2008 and 2000 authorize $400 million of general obligation debt to be issued to finance preservation of green space and natural areas, development of recreational trails, and protection of farmland through the purchase of agricultural easements, all through partnerships with local governments. Not more than $50 million may be issued in any fiscal year. Additional debt may be issued as outstanding debt is retired, provided that not more than $400 million is outstanding at any time.
Higher Education - A 1999 constitutional amendment authorizes general obligation debt to be issued to pay the cost of school buildings and related capital facilities for state-supported and state-assisted institutions of higher education. There is no constitutional limit on the amount of debt that can be outstanding at any time.
Infrastructure Improvements - A 2014 constitutional amendment authorized $1.875 billion of general obligation debt as a 10-year extension of this program to finance public infrastructure capital improvements of municipal corporations, counties, townships, and other local government entities as designated by law, with an annual issuance limit of $175 million in the first five years increasing to $200 million in the second five-years. This extension followed a prior 10-year extension passed in 2005 which authorized an additional $1.35 billion of general obligation debt. Additionally, there were two prior debt authorizations for this purpose (passed in 1985 and 1995) that each authorized $1.2 billion in debt.
Natural Resources - A 1993 constitutional amendment authorizes $200 million of general obligation debt to be issued to finance capital facilities for parks and natural resources improvements. Additional debt may be issued as outstanding debt is retired, provided that no more than $200 million is outstanding at any time. Not more than $50 million may be issued in any fiscal year. The full faith and credit, revenue (excluding net state lottery proceeds), and taxing power (excluding highway user receipts) of the state are pledged to retire this debt.
Site Development - A 2005 constitutional amendment authorizes the issuance of $150 million of general obligation debt for the development of sites for industry, commerce, distribution, and research and development by preparing those sites for immediate development by business prospects. Not more than $30 million was permitted to be issued in each of the first three fiscal years and not more than $15 million in any other fiscal year.
Third Frontier Research and Development - Constitutional amendments in 2010 and 2005 authorize the issuance of $1.2 billion of general obligation debt to provide grants to nonprofit and for-profit entities for research and development projects in support of Ohio industry, commerce and business. Project awards focus on biosciences, advanced materials, information technology, power and propulsion, and instruments-controls-electronics. No more than $450 million total may be issued in state fiscal years 2006 through 2011, no more than $225 million in fiscal year 2012 and no more than $175 million in any fiscal year thereafter.
Veterans’ Compensation - A 2009 constitutional amendment authorizes the issuance of state general obligation debt to provide compensation to persons who have served in active duty in the United States armed forces at any time during the Persian Gulf, Afghanistan, and Iraq conflicts. Not more than $200 million may be issued and no obligations may be issued later than December 31, 2013.
Treasurer of State
The Treasurer of State issues general obligation bonds for highway construction, as summarized below.
Highway (Capital Improvements) - A 1995 constitutional amendment authorizes the issuance of general obligation debt for construction for the cost of construction, reconstruction, or other improvements of highways, including those on the state highway system and urban extensions, those within or leading to public parks or recreations areas, and those within or leading to municipalities. The amendment provides that as this debt is retired additional debt may be issued so long as no more than $1.2 billion is outstanding at any time. No more than $220 million may be issued in any fiscal year. Though secured by the state’s full faith and credit, debt service has always been paid from pledged highway user receipts (including motor vehicle fuel tax receipts).
Special Obligation Lease-Rental Debt
As authorized for specified purposes by Section 2i of Article VIII of the Ohio Constitution, Special obligation bonds are secured by lease-rental payments that are subject to biennial appropriations from the state’s operating budgets. Special obligation bonds are not secured by a pledge of the state’s full faith and credit, and bondholders have no right to have taxes or excises levied by the General Assembly for the payment of debt service. Debt service payments are subject to biennial appropriations made in the benefiting agency’s operating budget pursuant to leases or agreements entered into by those agencies. The Treasurer of State is the current issuer of the state’s special obligation lease-rental bonds.
Treasurer of State
The Treasurer issues lease-rental obligations to house branches and agencies of state government or its functions, including facilities for mental health, parks and recreation, cultural and sports purposes, prisons and corrections, juvenile detention, and state office buildings and facilities for the Departments of Administrative Services, Transportation, and Public Safety and for the Bureau of Workers’ Compensation.
Debt service on special obligations is generally paid from the GRF, with the exception of debt issued for DOT and DPS facilities which is paid from highway user receipts.
Administrative Building Facilities - Provides financing for capital facilities to house branches and agencies of state government, including state office buildings and facilities.
Correctional Facilities - Provides financing for adult prisons and other correctional facilities (including juvenile detention facilities and community-based facilities) for state and certain local government entities.
Cultural and Sports Capital Facilities - Provides financing for grants administered by the Ohio Cultural Facilities Commission for cultural and sports capital facilities at Ohio’s non-profit theaters, museums, historical sites and publicly owned professional sport venues.
Mental Health Capital Facilities - Provides financing for state and community-based capital facilities for mental health and developmental disabilities purposes.
Parks and Recreation Capital Facilities - Provides financing for capital facilities for state and local parks and recreation.
Transportation and Highway Safety Buildings - Provides financing for capital facilities housing the Ohio Department of Transportation (ODOT) and the Ohio Department of Public Safety (DPS).
Debt service on these special obligations is paid from biennial appropriations from the state general revenue fund, except that debt service on obligations issued for ODOT and DPS facilities is payable from biennial appropriations of highway user
receipts, including the motor vehicle fuel tax.
Revenue Obligations Payable from Federal Title 23 Highway Funds
The Treasurer of State issues Major New State Infrastructure Project Revenue Bonds (also known as Grant Anticipation Revenue Vehicles or GARVEEs) to fund selected highway construction projects that have been approved by the U.S. Department of Transportation. The debt service charges on these bonds are secured by and payable primarily from Federal Title 23 Highway Funds received and to be received by the state, subject to biennial appropriations by the General Assembly.
Certificates of Participation
State agencies have also entered into lease-purchase agreements with terms ranging from 7 to 10 years primarily to finance information technology projects and capital equipment. Certificates of Participation (COPs) have been issued that represent fractionalized interests in or are payable from state payments made under those agreements. Payments by the state are subject to biennial appropriations by the General Assembly and the holders or owners of the COPs have no right to have excises or taxes levied to make those payments. The OBM Director’s approval of such agreements is required if COPs are to be publicly-offered in connection with those agreements. COPs have been issued to finance the acquisition and installation of the following information systems and equipment:
Bureau of Criminal Investigation Records System (BCIRS) - BCIRS is a criminal records management and biometric identification system administered by the Ohio Attorney General’s office that replaced the state’s computerized criminal history and automated fingerprint identification systems.
Enterprise Data Center Solutions (EDCS) - EDCS is an information technology program to expand and improve the state’s cloud computing environment and support upgrades to enterprise shared solutions.
Multi-Agency Radio Communications System Project (MARCS) - MARCS is a statewide computer and communications network administered by the Department of Administrative Services that is designed to provide instant voice and data communication and supply a communications backbone to the public safety and emergency management.
Ohio Administrative Knowledge System (OAKS) - OAKS which is an enterprise resource planning system was implemented to support the common back office operations of the state. The major statewide business functions supported by OAKS include capital improvements, financials, fixed assets, procurement, and human resources and payroll.
Ohio Attorney General Claims Fund Project (OAG) – OAG is a collection system for receiving and processing payments from over seven million active accounts. The system provides increased flexibility in collecting and managing payments, furthering compliance with federal guidelines.
State Taxation Revenue and Accounting System (STARS) - STARS is an integrated tax collection and audit system administered by the Ohio Department of Taxation that replaced the state’s separate tax software and administration systems.
Treasury Management System (TMS) - TMS is an integrated treasury technology infrastructure system that replaced the Treasurer of State’s separate cash, custody, investment, and accounting software and administration systems.
Unemployment Insurance System (UIS) - UIS is an unemployment insurance information and technology system for the use of the Department of Job and Family Services.
Voting Systems (VSA)- The voting systems acquisition program is administered by the Secretary of State’s office to acquire and implement new voting systems for all Ohio counties.
Revenue Bonds
Revenue bonds are used by the state to finance a specific project or category of projects. Debt service is secured by and paid from revenues or fees that are charged for the use of facilities. Various state authorities and commissions have been created by the General Assembly to issue revenue bonds. These include the Ohio Turnpike and Infrastructure Commission, the Ohio Housing Finance Agency, the Ohio Water Development Authority, and the Petroleum Underground Storage Tank Release Compensation Board. The funds borrowed by these authorities and the funds for the debt service payments on their obligations are outside the state treasury and are not appropriated by the legislature.
The Department of Development, the Ohio Water Development Authority, the Ohio Air Quality Development Authority, the Ohio Housing Finance Agency and the Ohio Higher Education Facilities Commission also issue conduit bonds for economic development, pollution control and solid waste, housing and private higher education projects. The debt service on those conduit bonds is paid solely by the benefited business or entity.
State Credit Enhancement Programs for School Districts and Community Technical Colleges
The state provides credit enhancement programs for school districts and two-year community and technical colleges to help reduce the cost of borrowing for certain capital projects. Under these programs, the state and the school district or college enter into an intercept agreement under which, in the event that debt service on the applicable debt obligations are not able to be made in full and on time, the state is authorized to withhold funds that would otherwise be paid to the school district or college and divert those funds to payment of debt service on the debt obligations. This credit enhancement typically results in a higher credit rating than the school district or college could obtain on a stand-alone basis. The higher credit rating enhances the security and improves the marketability of the bonds thereby resulting in a lower borrowing cost.
School Districts - The Ohio Department of Education administers the state’s credit enhancement program for school districts pursuant to Section 3317.18 of the Ohio Revised Code. That section, as further implemented by OAC rule 3301-8-1, sets forth the application requirements, eligibility criteria, and the procedural steps by which the intercept mechanism will be used for the payment of debt service in the event an institution is unable to make such payments. For additional information on the school district credit enhancement program, please contact the Ohio Department of Education.
Two-Year Community and Technical Colleges - The Ohio Department of Higher Education administers the state’s credit enhancement program for two-year community and technical colleges pursuant to Section 3333.59 of the Ohio Revised Code. That section, as further implemented by OAC Rule 3333-1-15, sets forth the application requirements, eligibility criteria, and the procedural steps by which the intercept mechanism will be used for the payment of debt service in the event a college is unable to make such payments. Under the program, colleges have the option of consolidating their separate issuances into a single offering issued by the Treasurer of State. For additional information on the community and technical college credit enhancement program, please contact the Ohio Department of Higher Education.
Types of State Issuers
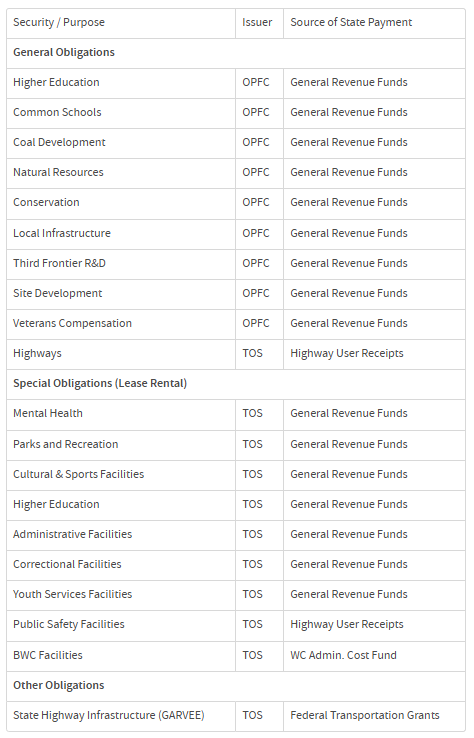
The state of Ohio has two primary issuers of debt for which the state is the direct obligor and debt service is paid from state revenues. These issuers are the Ohio Public Facilities Commission and the Treasurer of State. The table below shows the purposes of bonds issued by each and the source of state funds used to pay debt service on those bonds.
5% Debt Service Limitation
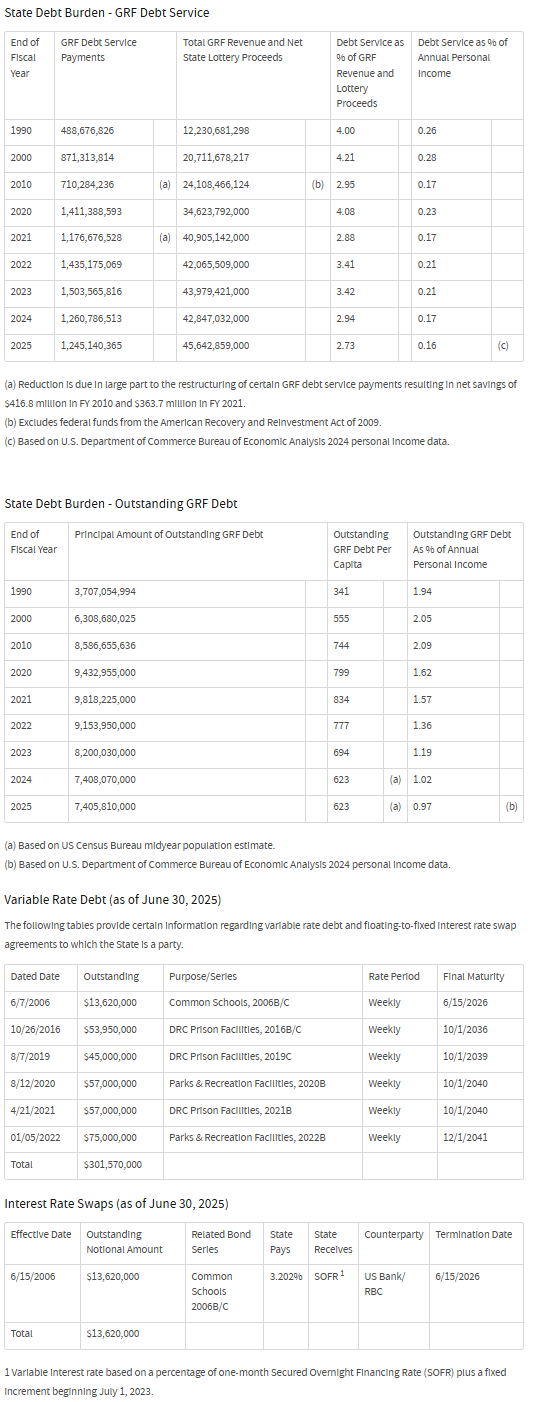
Section 17 of Article VIII of the Ohio Constitution, approved by Ohio voters in November 1999, establishes an annual debt service “cap” applicable to future issuance’s of state direct obligations payable from the general revenue fund (GRF) or net State lottery proceeds. Generally, new obligations may not be issued if debt service for any future fiscal year on those new and the then outstanding bonds of those categories would exceed 5 percent of the total of estimated GRF revenues plus net state lottery proceeds for the fiscal year of issuance.
Those direct obligations of the state include general obligation and special obligation bonds that are paid from the state’s GRF, but exclude (i) general obligation debt for Third Frontier Research and Development, development of sites and facilities, and veterans compensation, and (ii) general obligation debt payable from non-GRF funds (such as highway bonds that are paid from highway user receipts). Pursuant to the implementing legislation, the governor has designated the OBM Director as the State official responsible for making the 5 percent determinations and certifications. Application of the 5 percent cap may be waived in a particular instance by a three-fifths vote of each house of the Ohio General Assembly and may be changed by future constitutional amendments.
State Debt Profile
The following tables provide certain historical information and comparisons regarding debt outstanding and debt service. These tables reflect only then outstanding general and special obligation debt payable from the state’s GRF.